Hemophilia is a rare genetic disorder that affects the blood. Those who are afflicted with this condition lack two clotting factors – Factor VII or Factor IX – proteins within the blood that work in combination with platelets to stop bleeding. Hemophiliacs don’t produce enough of these clotting factors, and as a result, their blood does not have the ability to properly clot.
As mentioned, hemophilia is a genetic disorder or something that occurs as a result of an alteration in the genes; as such, the condition is either passed on from family member to family member (parents can pass it onto their children, for example), or the genetic change occurred during fetal development.
Hemophilia predominately affects males; females can also be affected, but it’s extremely rare Because hemophilia affects blood clotting, it’s a very serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. If you experience the following symptoms, see a doctor immediately.
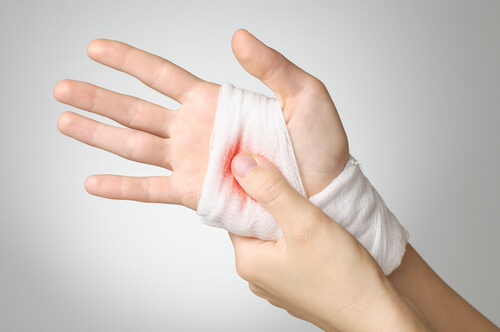
1. Excessive external bleeding.
When someone suffers an injury that breaks through the skin, bleeding naturally occurs. Under normal circumstances, the blood begins to clot immediately, thanks to the proteins, or clotting factors, mentioned about – Factor VII and Factor X. In individuals who are afflicted with hemophilia, however, clotting is extremely slowed or ineffective, as they lack sufficient levels of these proteins. As a result, even minor injuries can lead to excessive bleeding.
Tiny scratches and scarps can lead to massive amounts of blood loss. If you notice that any small injuries you sustain – paper cuts, tine scratches, etc – are bleeding a lot more and a lot longer than they should, there is a chance you could have hemophilia.
Because excessive blood loss is extremely dangerous and can be life-threatening, it is important that you seek immediate emergency medical care; do not, under any circumstances, put off seeing a doctor.