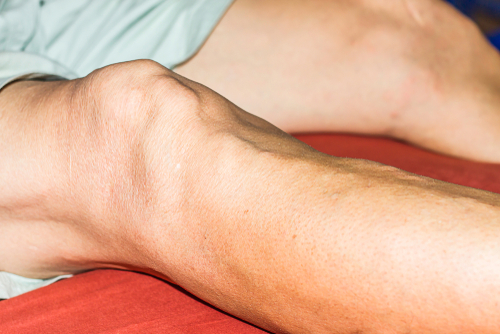
Synovial inflammation is also known as synovitis. This condition develops when the synovium portion of a joint in your body gets inflamed. In your joints, stratum synovial is an essential part of connective tissue that pads the capsule of your joints. The articular capsule of your joints look like a bubble, this bubble covers the joints in your body. The joint capsule covers joints on the wrist, elbow, shoulder, ankle, knee and all of your other joints.
There are two layers, one being the sturdy outer layer named the fibrous stratum, the other being the soft inside named the synovium. There is a fluid that resides in between both layers that are called synovial fluid.
The sole task of this fluid is to ensure that the joint stays lubricated and moist. Synovial fluid is highly viscous which helps to cut down on the amount of friction experienced by the articular cartilage when the joint is being moved
1. Gout
There are several types of arthritis, gout being the most common. Gout results in intense stiffness, swelling and pain in the joints most often the joint of the big toe. One of the main causes of synovitis, which is the inflammation of the joint, is gout. Attacks of gout are usually chronic and strike quickly without warning. Each attack harms the tissues of the joint by causing a severe case of synovitis. Almost all gout attacks are extremely painful.
There are several causes of gout including obesity, hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. Gout and the resulting synovitis are most often found in men, however, women are equally prone to developing it after menopause.
This form of arthritis is typically caused by having too much uric acid in the blood. Though synovitis from gout usually strikes the big toe, any joint in the body can be affected. Gout can be treated with medication and therapy.



