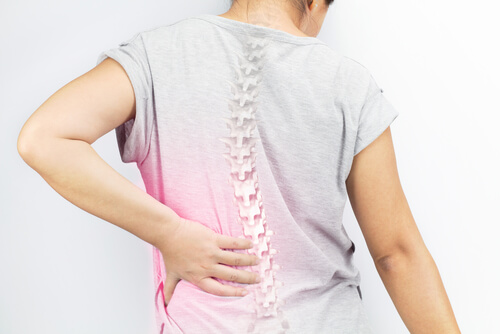
Scoliosis is a condition that will cause the spine to start to curve to one side. This condition can affect any area of the spine, but most commonly it occurs in the lower back and at the chest level. Scoliosis will often appear in children. Most of the time there is no treatment needed for scoliosis as the curve will begin to correct itself as the child grows.
However, the age of the child and the degree of the curvature will determine whether or not treatment is needed. There is a small number of people who suffer from scoliosis that will require surgery in order to fix the spine. There are some complications that can be caused by scoliosis. Some of these include respiratory deficiencies and chronic pain.
A person may also have a decrease in their exercise capacity. Here are some symptoms of scoliosis as well as preventative measures that can be taken.
1. Definition of Scoliosis
People who have scoliosis will have an S or C shaped curve in the spine. This condition may appear at any age. Most often it is found in children from ten to twelve years of age. It may also appear during the teen years. Some infants may show symptoms of scoliosis as well.
It is not typically known why the spine starts to change shape causing this syndrome to occur. In some cases, scoliosis is linked to a birth defect, spina bifida, muscular dystrophy, or cerebral palsy. Structural curves are permanent and could be caused by a different type of condition.
A nonstructural curve is often temporary and is likely to disappear in time. This is especially true when it occurs during the preteen or teen years as a child will likely grow and the curve will disappear. Physical therapy may be recommended to help the spine grow in the right direction.