Blood is comprised of several elements, and all of these elements play an important role in how blood functions and platelets are one of the most important elements. These blood cells are important because they help the blood clot.
When blood vessels become damaged, your body automatically sends these colorless blood vessels to the site of the injury, where they join together and create a clot. The platelets spread out across the surface of the injured blood vessels and stick to it, a process known as adhesion. As the platelets adhere to the surface of the injury, they stop the bleeding and the process of repairing the damage begins.
Platelets are formally known as thrombocytes. Some people have low levels of platelets, a condition is known as thrombocytopenia. Those who suffer from this condition bleed easily, as their blood does not clot effectively. The following symptoms are indicative of thrombocytopenia.
1. Easy bruising.
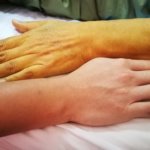
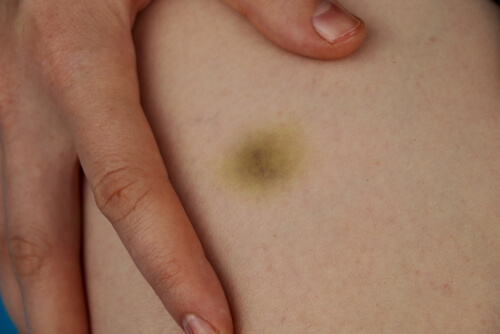
Bruises, also known as contusions or black and blues, occur as a result of an injury or trauma; banging into something with force, or being hit by something with force, for example. The trauma causes small blood vessels underneath the skin to burst, which leads to bleeding. The blood pools and becomes trapped underneath the surface of the skin, which results in the appearance of a bruise.
Everyone experiences bruised at one point or another and they’re very common. You may know exactly what caused a bruise (being hit by a ball, for example), or you may not remember the injury that caused the bruise; however, in either cause, a pretty forceful blow will cause the bruise.
If you have low platelets, however, you may develop bruises very easily; gently rubbing against something, or even something as simple as your pants rubbing against your hips, for example.