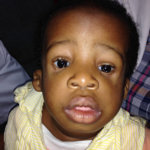
A member of the poxvirus family, Molluscum contagiosum is a highly contagious virus that thrives in warm and humid climates. It is also very prevalent in places where people live in close quarters, either by the practice of culture or the necessity of poverty.
The virus manages to infect people via small breaks in the skin’s surface, sometimes not even visible to the naked eye. A lot of people have immunity to the virus, and so may never experience symptoms, but for many other people who have no resistance, the typical growths of the infection will start to become visible between 2 to 8 weeks after the initial infection.
The virus spreads very easily and children are amongst the most likely of demographics to pick it up and spread it, given their tendency to be very hands-on and their lack of hygiene which is dependent on their stage of development and social circumstances. Here are 8 things to bear in mind about Molluscum contagiosum.
1. Can be spread between sexual partners
Whilst it is most often children who become infected with Molluscum contagiosum, it is true that sexual contact can spread the virus between adults and teens. This virus is not always categorized as a sexually transmitted disease, although in some quarters it is, given that sexually active people may contract the virus through close skin to skin contact.
It doesn’t have to be sexual contact though, which causes it to spread, and so there is no need for moral panic whenever a child is diagnosed. This ‘need to know’ information about Molluscum contagiosum is purely for public knowledge, and is by no means an assessment as to how a person picked up the infection.
In truth, children are likely to pick it up from touching toys, clothes, objects, and surfaces, as well as other children who may be infected. It is true though, that sexual contact can cause the virus to spread between sexually active people, hence it’s listing here.