Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory disease. In patients with sarcoidosis, granulomas — a fancy word for inflammatory cells — will begin to grow and collect in a certain region of your body. The two most common targets of sarcoidosis are the lymph nodes and lungs. That being said, it can also adversely impact your other organs such as the heart, skin, eyes, and more. As of the present date, the exact cause of sarcoidosis remains unknown to doctors.
That being said, some experts have suggested the possibility that it develops as a result of the immune system trying to fight off unknown substances. There have been some studies showing that chemicals, infectious agents, dust, and atypical reactions to proteins in the body may be the cause of the formulation of these granulomas — particularly in patients with a genetic predisposition. Here are eight of the most common symptoms.
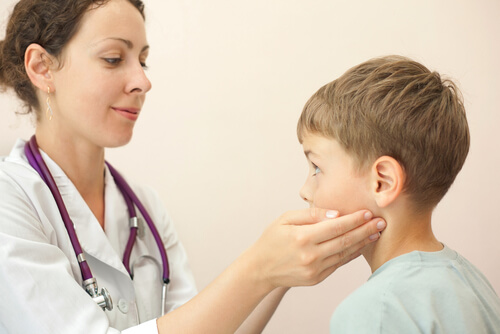
1. Swollen lymph nodes
Many viruses and bacteria could lead to the swelling of your lymph nodes, and sarcoidosis is no exception. While swollen lymph nodes are often associated with cancer, it’s actually relatively rare for them to be of cancer-related origin.
Some cases of swelling will be localized to a specific area. In other cases where the swelling of lymph nodes is more generalized throughout your entire body then you may be dealing with an infection like HIV or an immune disorder such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
Doctors often don’t rely on swollen lymph nodes for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis due to the fact that so many different viruses can cause it. In fact, measles, strep throat, and tuberculosis can all also cause swollen lymph nodes, making it an unreliable indicator of sarcoidosis.